一、基本概念 队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,元素在队列尾追加,而从队列头删除。而在优先队列(Priority Queue) 中,元素被赋予优先级。当访问元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除 。优先队列具有最高级先出 (first in, largest out)的行为特征。通常采用堆 这种数据结构来实现。
通常,优先队列包括最大优先队列 和最小优先队列 。最大优先队列可以确保每次获取到整个队列中的最大元素并将其删除,而最小优先队列则确保每次获取到整个队列中的最小元素并将其删除。
二、具体实现 1、基本功能 我们可以创建一个PriorityQueue<E>类来表示优先队列,下面将分别介绍一下该类的成员变量和公共方法:
成员变量
成员名
类型
说明
queueObject[]用于存放队列中的元素
sizeint当前队列中元素的个数
comparatorComparator<? super E>比较器,用于支持自定义比较
公共方法
方法名及参数
返回值类型
说明
isEmpty()boolean判断队列是否为空
size()int获取队列中的元素个数
offer(E e)boolean向队列中插入一个元素
poll()E获取队首元素并将其从队列中移除
peek()E获取队首元素但保留该元素
该部分的代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 public class PriorityQueue <E > private Object[] queue; private int size; private Comparator<? super E> comparator; public PriorityQueue (int capacity) this (capacity, null ); } public PriorityQueue (int capacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator) if (capacity < 1 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this .queue = new Object[capacity]; this .comparator = comparator; } public boolean isEmpty () return size == 0 ; } public int size () return size; } public boolean offer (E e) int i = size; if (i == queue.length) return false ; size = i + 1 ; if (i == 0 ) queue[0 ] = e; else shiftUp(i, e); return true ; } public E poll () if (size == 0 ) return null ; int s = --size; E result = (E) queue[0 ]; E x = (E) queue[s]; queue[s] = null ; if (s != 0 ) shiftDown(0 , x); return result; } public E peek () return size == 0 ? null : (E) queue[0 ]; } }
在上面的代码中使用了shiftUp和shiftDown方法,它们分别表示上移和下移,下面将重点介绍这两个方法是如何实现的。
2、上移 如果在普通的队列中插入一个元素是非常容易的,只需将其插入队尾即可。但在优先队列中,除了将其插入队列中,还要确保插入元素后整个队列仍然保持优先队列的性质。这时,我们就需要通过上移操作来实现优先队列的插入操作。下面将通过实例来介绍上移操作的具体过程。
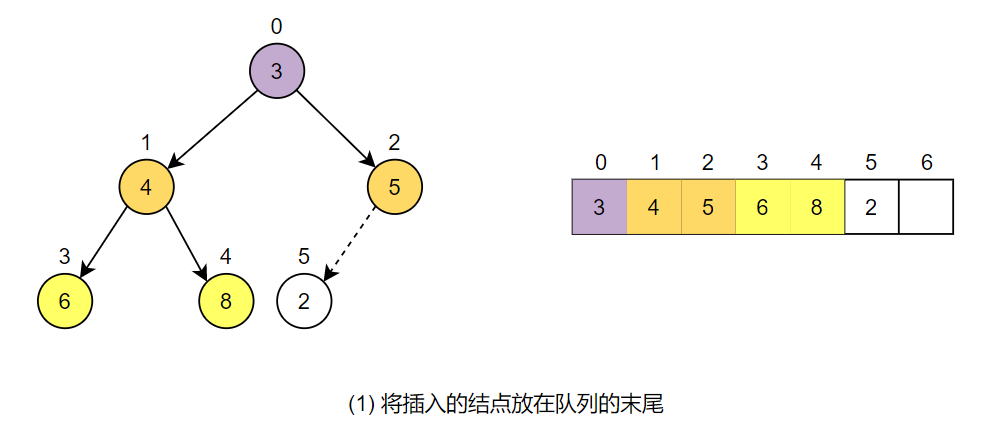
假设有一个优先队列${3,4,5,6,8}$,现在需要插入结点2。首先将新插入的结点放在队列的末尾,如下图所示:
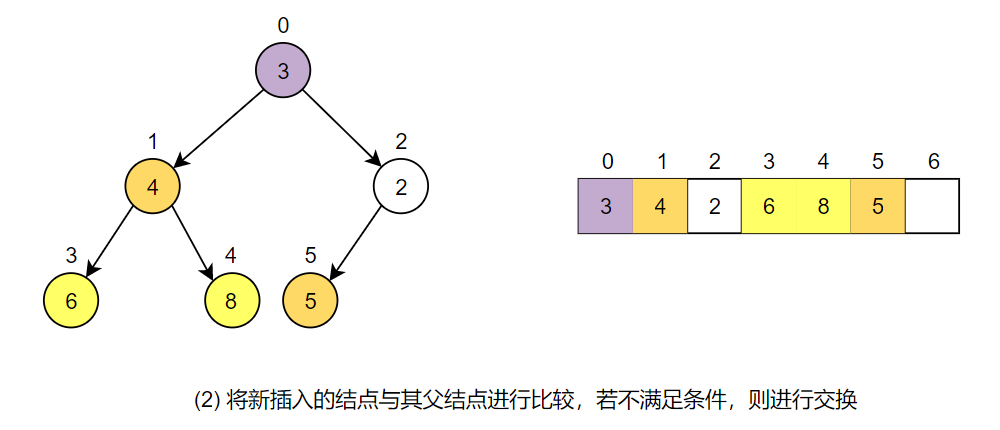
之后将新插入的结点与其父结点进行比较。该例中新插入的结点所在位置的索引为 5,因此其父结点的索引为$(5-1)/2 = 2$,在索引为 2 的结点值为 5,由于该队列是最小优先队列,因此需要将新插入的结点与其父结点进行交换。
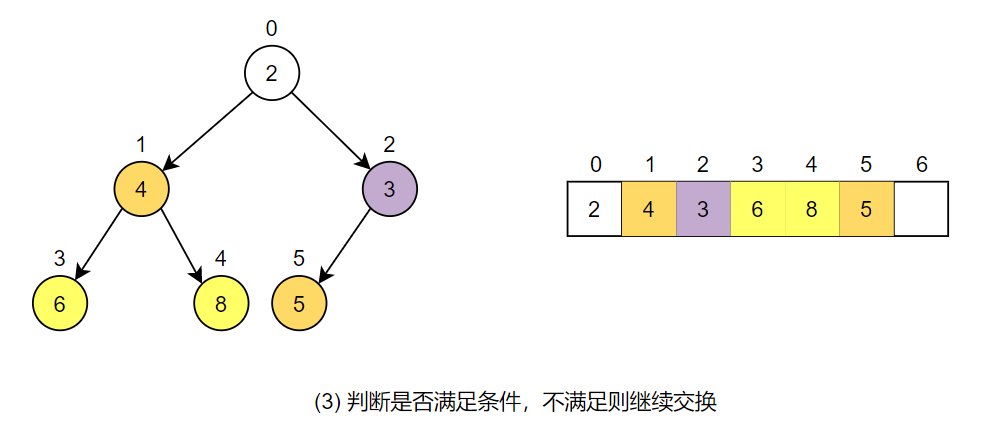
继续判断是否满足优先队列的条件。此时新插入结点的索引为 2,因此其父结点的索引为$(2-1)/2=0$,此处的值为 3,仍不满足条件,再次进行交换。
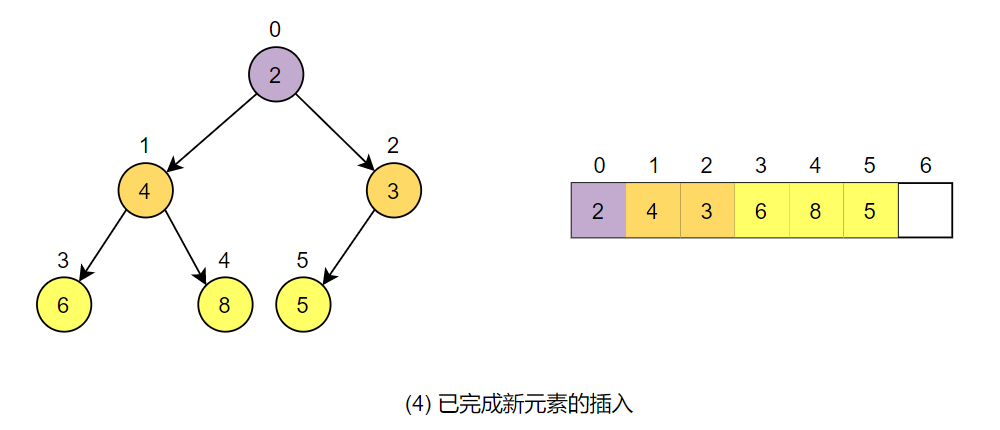
此时满足优先队列的条件,完成插入。
上移操作的代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 private void shiftUp (int k , E e) if (comparator != null ) { while (k > 0 ) { int parent = (k-1 ) >>> 1 ; Object elem = queue[parent]; if (comparator.compare(e, (E) elem) >= 0 ) break ; queue[k] = elem; k = parent; } queue[k] = e; } else { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) e; while (k > 0 ) { int parent = (k-1 ) >>> 1 ; Object elem = queue[parent]; if (key.compareTo((E) elem) >= 0 ) break ; queue[k] = elem; k = parent; } queue[k] = e; } }
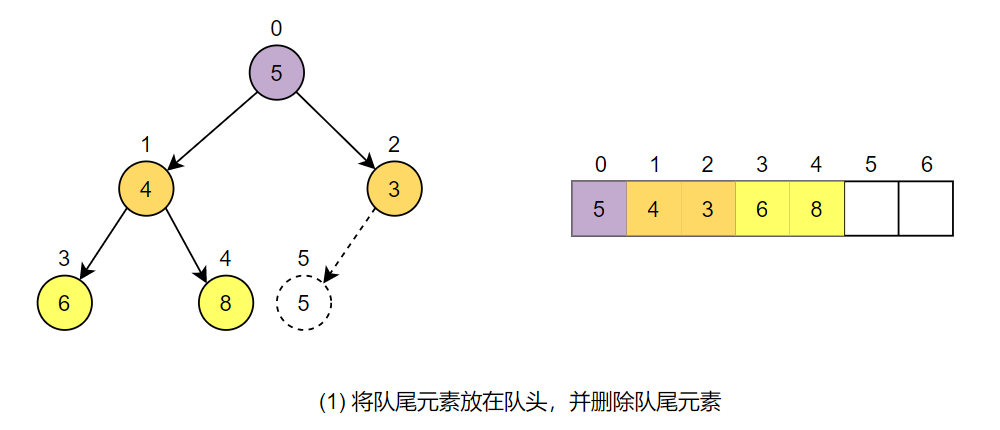
3、下移 当删除优先队列中的元素时,首先返回队首元素,之后将队尾元素放在队首,并删除队尾。之后通过下移操作调整队列,使其满足条件。下面将通过实例来说明下移操作的完整过程。
接着上面的例子,假设需要删除 2,首先将队首元素 2 保存起来作为结果返回,并将队尾元素 5 放在队首,并删除队尾元素。
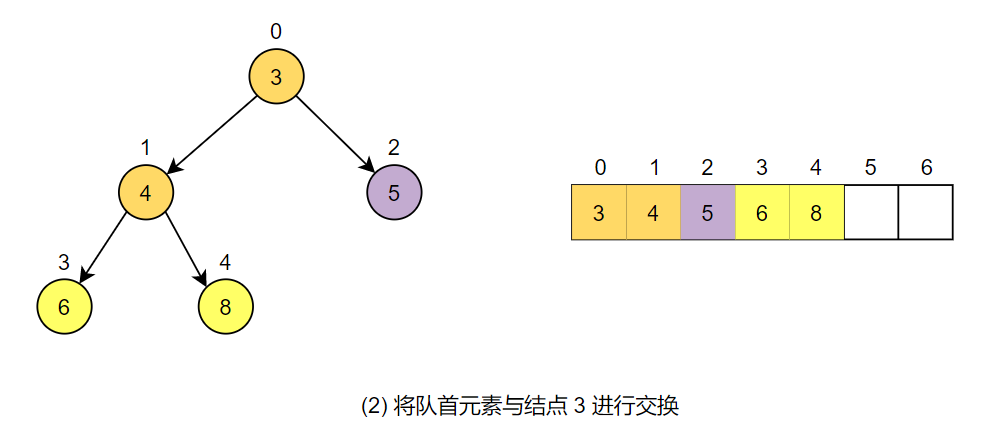
之后对队首结点的两个孩子进行比较(若右孩子存在),选择优先级最小的结点(这里是结点 3)与队首结点进行比较,因为队首元素的优先级大于结点 3,因此将这两个结点进行交换。
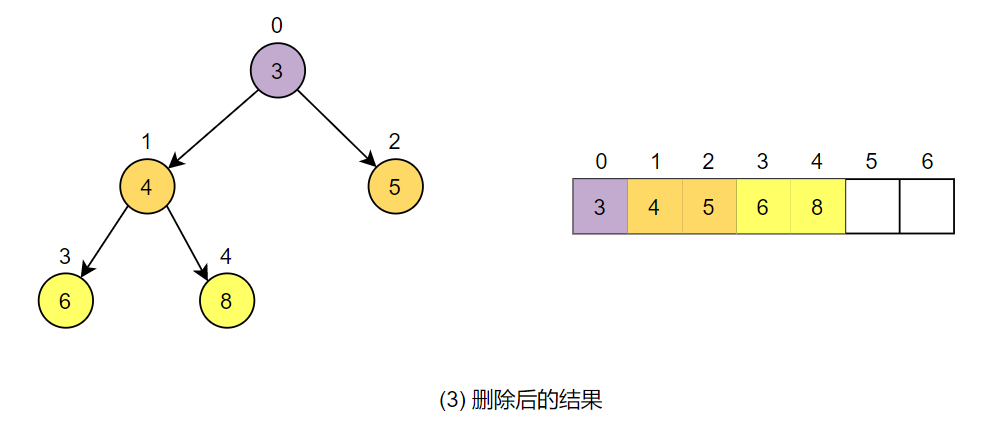
由于此时原队首元素已经是叶子结点,因此下移操作结束,整个删除操作完成。
下移操作的代码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 private void shiftDown (int k, E e) if (comparator != null ) { int half = size >>> 1 ; while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1 ) + 1 ; Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1 ; if (right < size && comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0 ) c = queue[child = right]; if (comparator.compare(e, (E) c) <= 0 ) break ; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = e; } else { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)e; int half = size >>> 1 ; while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1 ) + 1 ; Object c = queue[child]; int right = child + 1 ; if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0 ) c = queue[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0 ) break ; queue[k] = c; k = child; } queue[k] = key; } }
优先队列的完整实现已上传到 Gitee,仓库地址:https://gitee.com/fzcoder/data-structure-and-algorithms-demo 。
三、总结 优先队列与普通的队列相似,但可以确保每次出队的元素是当前队列中的最大(或最小)元素,可使用于需要获取最大的 K 个元素等情况。